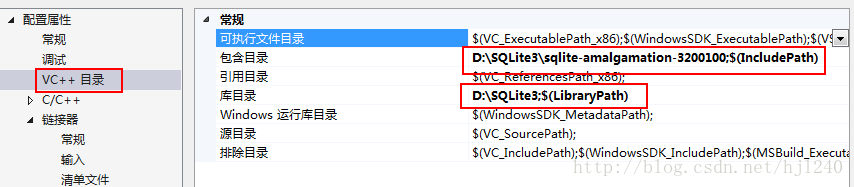
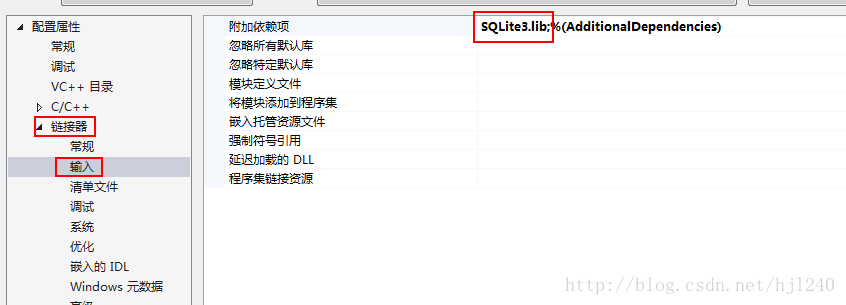
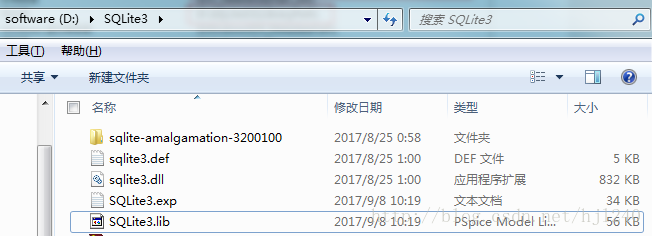
HMAC: Hash-based Message Authentication Code,即基于Hash的消息鉴别码
这周开始将图片上传、图片下载迁移到OSS上,在调用OSS的时候需要根据规则使用Hmac Sha1+BASE64对图片的一些数据进行计算token再上传,遇到了一个困扰一周的坑。
在生成token的规则中要求将sign_str加上一个换行符(\n)再进行Hmac Sha1计算,给的Python Demo如下:
sign_str = “{}?{}\n”.format( req_path , query_str )
b64_enc_sign_str = hash_hmac (sign_str , secret_key)
然后我直接在C++项目中
#include<openssl/hmac.h>
…
HMAC (EVP_sha1() , ch , strlen(ch) , data , dataLength , digest , &digest_len);
其中data是一个unsigned char*类型的数据,由字符串转化而来,而字符串的末尾加上了换行符,发现相同的加密串,相同的密钥,使用openssl中的Hmac和Python demo中的计算结果截然不同,然而都不加换行符的话计算结果则一模一样。
最后通过github寻找现成的Hmac_Sha1加密算法才得以解决。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
unsigned long Rol(unsigned long x, int y);
unsigned long Ror(unsigned long x, int y);
unsigned long f(unsigned long B,unsigned long C,unsigned long D, int t);
unsigned long H[5];
unsigned long T[512]={0};
void HMAC(string text, string key);
void SHA1(string s);
// HMAC function
int i;
void HMAC(string text, string key)
{
char c;
string s;
unsigned long Key[16] = {0};
unsigned long X[16] = {0};
unsigned long Y[16] = {0};
unsigned long ipad = 0x36363636;
unsigned long opad = 0x5c5c5c5c;
int k;
s = "";
//Process string key into sub-key
//Hash key in case it is less than 64 bytes
if (key.length() > 64)
{
SHA1(key);
Key[0] = H[0];
Key[1] = H[1];
Key[2] = H[2];
Key[3] = H[3];
Key[4] = H[4];
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<16; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (4*i+j <= key.length())
{
k = key[4*i+j];
}
else
{
k = 0;
}
if (k<0)
{
k = k + 256;
}
Key[i]= Key[i] + k*pow(256,(double)3-j);
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<16; i++)
{
X[i] = Key[i]^ipad;
Y[i] = Key[i]^opad;
}
//Turn X-Array into a String
for(i=0; i<16; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
c = ((X[i] >> 8*(3-j)) % 256);
s = s + c;
}
}
//Append text to string
s = s + text;
//Hash X-Array
SHA1(s);
s = "";
//Turn Y-Array into a String
for(i=0; i<16; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
c = ((Y[i] >> 8*(3-j)) % 256);
s = s + c;
}
}
//Append Hashed X-Array to Y-Array in string
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
c = ((H[i] >> 8*(3-j)) % 256);
s = s + c;
}
}
//Hash final concatenated string
SHA1(s);
}
// SHA-1 Algorithm
void SHA1(string s)
{
unsigned long K[80];
unsigned long A,B,C,D,E,TEMP;
int r,k,ln;
H[0]=0x67452301;
H[1]=0xefcdab89;
H[2]=0x98badcfe;
H[3]=0x10325476;
H[4]=0xc3d2e1f0;
ln=s.length();
r = int((ln+1)/64);
if (((ln+1) % 64) > 56)
{
r=r+1;
}
// initialize Constants
for(int t=0; t<80; t++)
{
if (t<20)
{
K[t] = 0x5a827999;
}
if ((t>19)&(t<40))
{
K[t] = 0x6ED9EBA1;
}
if ((t>39)&(t<60))
{
K[t] = 0x8F1BBCDC;
}
if (t>59)
{
K[t] = 0xca62c1d6;
}
}
for(int l=0; l <= r; l++)
{
unsigned long W[80]={0};
//Initialize Text
for (int i=0; i<16; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
if (4*i+j <= ln)
{
k = s[64*l+4*i+j];
}
else
{
k = 0;
}
if (k<0)
{
k = k +256;
}
if (4*i+j == ln)
{
k = 0x80;
}
W[i]= W[i] + k*pow(256,(double)3-j);
}
}
if ((W[14]==0)&(W[15]==0))
{
W[15]=8*s.length();
}
// Hash Cycle
for (int t = 16; t <80; t++)
{
W[t] = Rol(W[t-3]^W[t-8]^W[t-14]^W[t-16],1);
}
A = H[0];
B = H[1];
C = H[2];
D = H[3];
E = H[4];
for(int t = 0; t < 80; t++)
{
TEMP = Rol(A,5) + f(B,C,D,t) + E + W[t] + K[t];
E = D;
D = C;
C = Rol(B,30);
B = A;
A = TEMP;
}
H[0] = H[0] + A;
H[1] = H[1] + B;
H[2] = H[2] + C;
H[3] = H[3] + D;
H[4] = H[4] + E;
ln = ln - 64;
}
}
unsigned long f(unsigned long B,unsigned long C,unsigned long D, int t)
{
if (t < 20)
{
return ((B & C)^((~B) & D));
}
if ((t > 19) & (t < 40))
{
return (B ^ C ^ D);
}
if ((t > 39) & (t < 60))
{
return ((B & C)^(B & D)^(C & D));
}
if (t > 59)
{
return (B ^ C ^ D);
}
}
unsigned long Rol(unsigned long x, int y)
{
if (y % 32 == 0) {return x;}
else {return ((x << y)^(x >> -y));}
}
unsigned long Ror(unsigned long x, int y)
{
if (y % 32 == 0) {return x;}
else {return ((x >> y)^(x << -y));}
}
int main()
{
HMAC("helloworld\n","q4mJAS777BUbbdVpEqh2XRcZZqNyDweU4GRnM690");
int i = 0;
for(i = 0;i < 5;i++)
{
printf("%.8X\n",H[i]);
}
}
然后以为这一关就过了。。。然后在进行Base64加密的时候又遇到了一个坑。
给出的Python demo的代码如下:
b64_enc_sign_str = base64.b64encode( hmac_code ).decode()
然后我使用常规的Base64算法进行计算,又发现两个相同的字符串进行加密后得到的结果大相径庭。
最后在 https://1024tools.com/hmac 找到了原因,常规的Base64算法就像 https://blog.csdn.net/wo541075754/article/details/81734770 所说,而我们这里需要将HMAC计算返回的原始二进制数据后进行Base64编码。
首先将HMAC_Sha1加密得出的结果转换为二进制编码。
void CCommonFunction::HexToBin(CString hexDight , CString& binDight){
binDight = "";
int f = 0,c = 0;
char e;
for(int f = 0; f <= hexDight.GetLength() ; f++){
e = hexDight[f];
if(e >= 'a' && e <= 'f'){
int a = static_cast<int>(e-'a'+10);
switch(a){
case 10 : binDight = binDight + "1010";
break;
case 11 : binDight = binDight + "1011";
break;
case 12 : binDight = binDight + "1100";
break;
case 13 : binDight = binDight + "1101";
break;
case 14 : binDight = binDight + "1110";
break;
case 15 : binDight = binDight + "1111";
break;
}
}
else if( e >= '0' && e <= '9'){
int b = static_cast<int>(e-'0');
if(f == 0){
switch(b){
case 0:
break;
case 1: binDight = binDight + "1";
break;
case 2: binDight = binDight + "10";
break;
case 3: binDight = binDight + "11";
break;
case 4: binDight = binDight + "100";
break;
case 5: binDight = binDight + "101";
break;
case 6: binDight = binDight + "110";
break;
case 7: binDight = binDight + "111";
break;
case 8: binDight = binDight + "1000";
break;
case 9: binDight = binDight + "1001";
break;
}
}
else{
switch(b){
case 0 : binDight = binDight + "0000";
break;
case 1: binDight = binDight + "0001";
break;
case 2: binDight = binDight + "0010";
break;
case 3: binDight = binDight + "0011";
break;
case 4: binDight = binDight + "0100";
break;
case 5: binDight = binDight + "0101";
break;
case 6: binDight = binDight + "0110";
break;
case 7: binDight = binDight + "0111";
break;
case 8: binDight = binDight + "1000";
break;
case 9: binDight = binDight + "1001";
break;
}
}
}
}
}
然后判断二进制串是否是6的倍数,不是6的倍数的话在末尾补0直到该二进制串是6的倍数,然后每6位取一次6位的二进制串,转换为10进制,然后去Base64编码对照表中找出这个十进制数字对应的字符,将这些所有的字符拼接起来并在末尾加上一个固定的“=”即可,代码如下:
//Base64编码表
const char Base64EncodeMap[64] =
{
'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H',
'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P',
'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X',
'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f',
'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n',
'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v',
'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', '0', '1', '2', '3',
'4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '+', '/'
};
void CCommonFunction::BinToBase64(CString binStr , CString &base64Str)
{
while(binStr.GetLength() % 6 != 0){
binStr = binStr + "0";
}
base64Str = "";
CString tmp = "";
int index = 0;
int num = 0;
while(index < binStr.GetLength()){
tmp = binStr.Mid(index , 6);
index = index + 6;
num = BinToDecInt(tmp);
base64Str = base64Str + Base64EncodeMap[num];
}
base64Str = base64Str + "=";
}